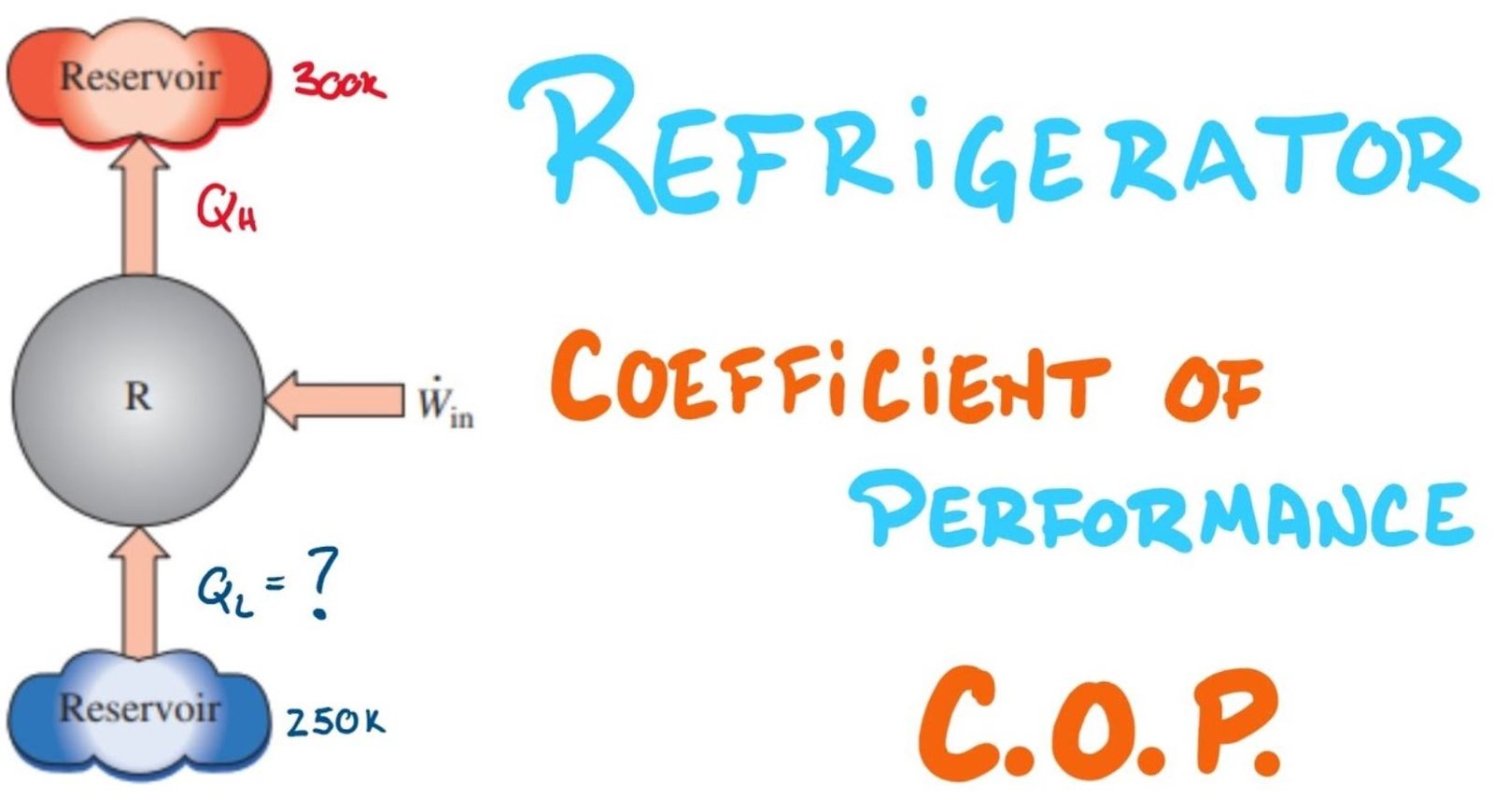
Generally, cooling systems where refrigerants are used (such as refrigerators, air conditioners) or heat pumps are referred to as the Coefficient of Performance in air conditioning applications and are briefly shown as COP. COP is the ratio of the heating or cooling amounts of the systems to the given energy (or required work).
When calculating the Coefficient of Performance (COP), the heat output (Q) from the condenser is proportional to the power (W) supplied to the compressor.
Coefficient of Performance (COP)
COP is defined as the relationship between the power (kW) drawn as cooling or heating from the heat pump or cooling/heating system and the power (kW) supplied to the compressor.
Coefficient of Performance (COP) evaluates the performance of heating or cooling systems and calculates their efficiency. A higher COP value means higher efficiency.
The following points include the features of COP:
- It is the ratio of cooling/heating output to compressor power.
- If the coefficient of performance (COP) increases, more cooling/heating is achieved for the same compressor power.
- If COP increases, it becomes a more efficient system.
- If COP increases, productivity increases, while COP decreases decreases efficiency.
- The higher the COP, the less energy consumed for unit cooling and lower operating costs.
Formula of Coefficient of Performance (COP)
Coefficient of Performance is basically found by dividing the output by the input. The formula is as follows.
COP = Output / Input
Coefficient of Performance for heating is,
K = QH / Win
Where,
K = Coefficient of Performance,
QH = The heat pump’s output,
Win = The work required by the considered system.
Coefficient of Performance for cooling is,
K = QC / Win
Where,
K = Coefficient of Performance,
QC = the refrigerator’s heat had dissipated,
Win = The work required by the considered system.
If the Work input is zero then the Coefficient of Performance is equal to infinity.
COP of Refrigerator is,
KR = Q2 / (Q1 – Q2)
For reversible Refrigerator,
Q1/Q2 = T1/T2
KR = T2 / (T1 – T2)
- COP of Heat pump,
KH = Q1 / (Q1 – Q2)
For reversible Heat pump,
Q1/Q2 = T1/T2
KH = T1 / (T1 – T2)
How Improving the COP
Some minor points can be applied to improve COP.
- As the formula shows, the COP of a heat pump system can be improved by reducing the temperature gap
and
at which the system works.
- Outdoor temperature has a great effect on the change of COP. For this reason, the condenser unit should be positioned where it will not receive direct sunlight.
- Keeping the condenser and evaporator pads clean and preventing air passage will increase the cooling / heating capacity and increase the COP.
- During the installation of the system, the required capacity should be installed with correct calculation. Cooling or heating systems installed at capacities larger or smaller than required will operate inefficiently.
- When the condenser is water cooled or ground cooled, the cooling amount will increase and the COP will increase as the condenser temperature will decrease.