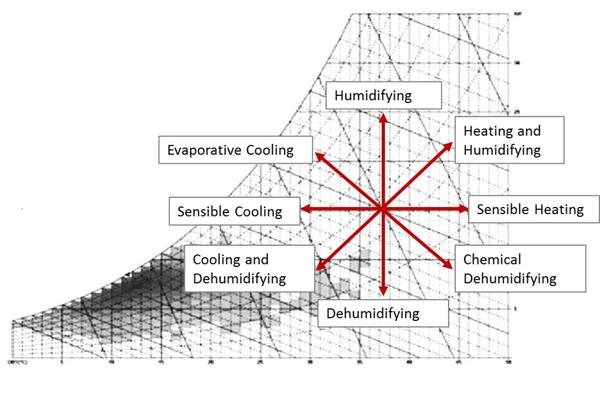
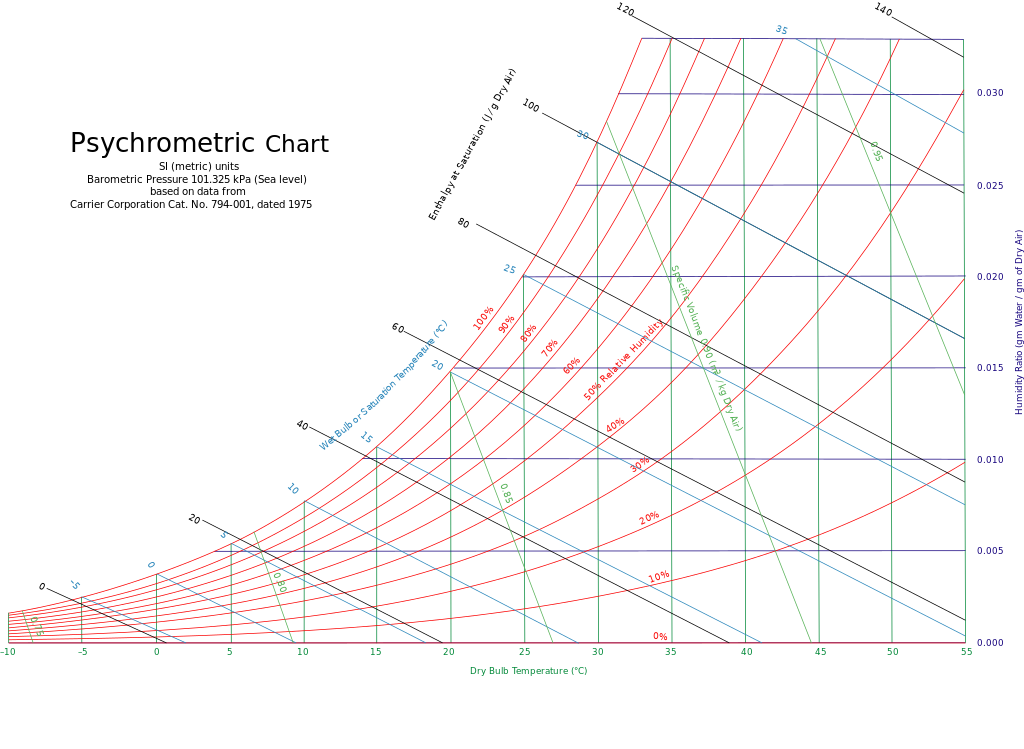
Psychrometric Chart is the tool most used by engineers to find out the tool of air. If two properties of air are known, all other properties can be found with the psychrometric diagram. You can perform operations on the air with the features available. (For example, heating, cooling, humidification, etc.)
Air properties that can be found with a psychrometric chart
If two properties of air are known, all other properties can be found with the psychrometric chart.
- Dry-bulb temperature (DBT)
- Wet-bulb temperature (WBT)
- Dew point temperature
- Humidity
- Specific Humidity
- Absolute humidity
- Relative humidity
- Specific enthalpy
- Specific volume
- Psychrometric ratio
- Humid heat
- Pressure
Before explaining the properties of the above air in detail, let’s share the psychrometric chart.
Let’s examine the properties of air through the psychrometric chart.
Dry-bulb temperature (DBT)
The dry-bulb temperature is the temperature indicated by a thermometer exposed to the air in a place sheltered from direct solar radiation. The term dry-bulb is customarily added to temperature to distinguish it from wet-bulb and dew point temperature.
Dry-bulb temperature (DBT) is that of an air sample, as determined by an ordinary thermometer. It is typically plotted as the abscissa (horizontal axis) of the graph.
Wet-bulb temperature (WBT)
The thermodynamic wet-bulb temperature is a thermodynamic property of a mixture of air and water vapor. The value indicated by a wet-bulb thermometer often provides an adequate approximation of the thermodynamic wet-bulb temperature.
Wet-bulb temperature (WBT) is that of an air sample after it has passed through a constant-pressure, ideal, adiabatic saturation process, that is, after the air has passed over a large surface of liquid water in an insulated channel. In practice this is the reading of a thermometer whose sensing bulb is covered with a wet sock evaporating into a rapid stream of the sample air (see Hygrometer). When the air sample is pre-saturated with water, the WBT will read the same as the DBT. The slope of lines of constant WBT is the ratio between the heat of vaporization of water and the specific heat of dry air, roughly 0.4.
Dew point temperature
The saturation temperature of the moisture present in the sample of air, it can also be defined as the temperature at which the vapour changes into liquid (condensation). Usually the level at which water vapor changes into liquid marks the base of the cloud in the atmosphere hence called condensation level.
Dew point temperature (DPT) is the temperature at which a moist air sample at the same pressure would reach water vapor “saturation.” At this point further removal of heat would result in water vapor condensing into liquid water fog or, if below freezing point, solid hoarfrost.
Humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Absolute humidity
The mass of water vapor per unit mass of dry air containing the water vapor. This quantity is also known as the water vapor density.[
Relative humidity
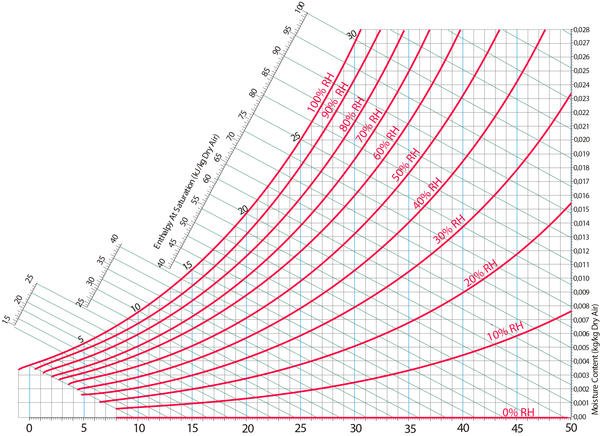
Relative humidity (RH) is the ratio of the mole fraction of water vapor to the mole fraction of saturated moist air at the same temperature and pressure. RH is dimensionless, and is usually expressed as a percentage.
Specific enthalpy
Analogous to the specific enthalpy of a pure substance. In psychrometrics, the term quantifies the total energy of both the dry air and water vapour per kilogram of dry air.
Specific volume
Analogous to the specific volume of a pure substance. However, in psychrometrics, the term quantifies the total volume of both the dry air and water vapour per unit mass of dry air.
Psychrometric ratio
The psychrometric ratio is the ratio of the heat transfer coefficient to the product of mass transfer coefficient and humid heat at a wetted surface. It may be evaluated with the following equation:
- where:
-
- = Psychrometric ratio, dimensionless
- = convective heat transfer coefficient, W m−2 K−1
- = convective mass transfer coefficient, kg m−2 s−1
- = humid heat, J kg−1 K−1
Humid heat
Humid heat is the constant-pressure specific heat of moist air, per unit mass of the dry air. The Humid Heat is the amount of Heat required to change the temperature of unit mass of a Water Vapor – Air Mixture by 1 °C.
Psychrometric Chart Source: Wikipedia
-