SketchUp and PVsyst are the two most used programs in the solar industry. When their powers are combined, a great simulation emerges.
During the design and installation of solar power plants, advanced software tools are needed to analyze and optimize. Two of the most commonly used tools in this field are SketchUp and PVsyst. While SketchUp is famous for its intuitive 3D modeling capabilities, PVsyst is a specialized software for simulating and analyzing PV systems. Used together, these tools create a powerful combination for designing accurate, efficient, and visually appealing solar power installations.
In this article, we will examine the relationship between SketchUp and PVsyst, highlighting how these platforms complement each other and detailing the workflow that integrates their capabilities for solar energy projects.
Overview of SketchUp and PVsyst
SketchUp: 3D Design Made Simple

SketchUp is a user-friendly 3D modeling tool popular among architects, engineers, and designers. It allows users to create detailed three-dimensional representations of structures and landscapes. In solar energy projects, SketchUp is often used to model buildings, rooftops, and terrain, providing a realistic environment for designing PV systems.
PVsyst: Advanced Solar System Simulation

PVsyst, on the other hand, is a specialized software designed for the study, sizing, and analysis of PV systems. It enables users to simulate energy production, evaluate shading losses, and analyze the economic performance of solar installations. Its detailed modeling features are essential for accurately predicting the performance of PV systems under various conditions.
Why Combine SketchUp and PVsyst?
While SketchUp and PVsyst serve different purposes, their integration offers significant advantages:
- Enhanced Visualization: SketchUp’s 3D modeling provides a visually rich representation of PV systems in their real-world settings, aiding in project presentations and stakeholder communication.
- Accurate Shading Analysis: By exporting SketchUp models to PVsyst, users can incorporate detailed shading objects (e.g., trees, buildings, or obstructions) into the PV simulation for precise shading loss calculations.
- Streamlined Workflow: The seamless transfer of data between SketchUp and PVsyst reduces manual work, minimizing errors and improving design accuracy.
Workflow: From SketchUp to PVsyst
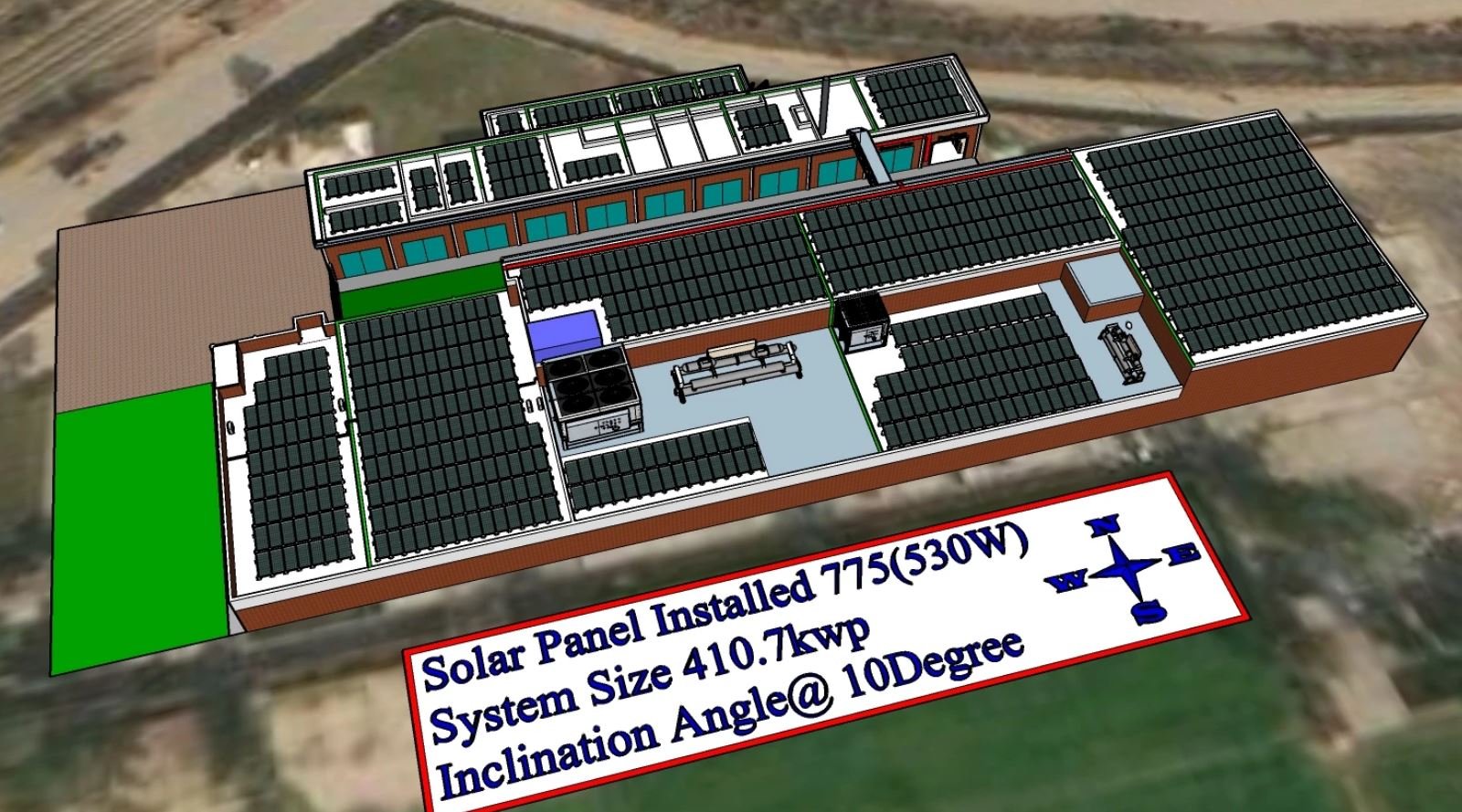
Step 1: Creating the 3D Model in SketchUp
The process begins with developing a detailed 3D model of the site in SketchUp. This model may include:
- Rooftops, walls, and building structures.
- Terrain profiles for ground-mounted systems.
- Potential obstructions such as trees, chimneys, or adjacent buildings.
Step 2: Exporting the Model to PVsyst
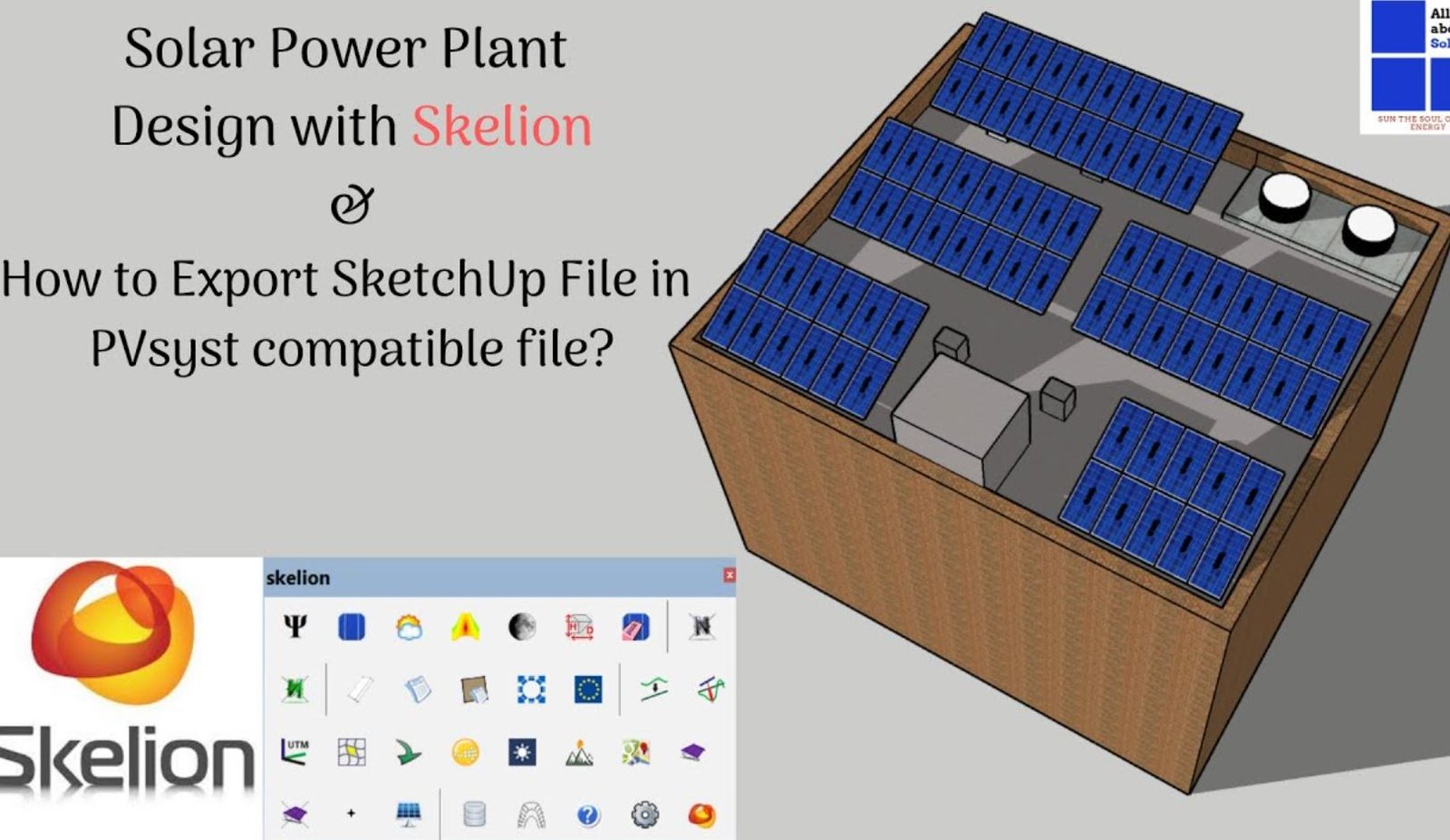
Once the SketchUp model is ready, it can be exported to PVsyst using a compatible format. The most commonly used method is exporting the SketchUp model as a .DXF file or using specialized plugins such as Helios3D or other SketchUp extensions for solar design.
Step 3: Importing into PVsyst
In PVsyst, the 3D model is imported into the Shading Scene Construction tool. Users can align the imported objects with the PV array layout and define shading objects. PVsyst uses this shading scene to calculate:
- Near Shading Losses: These are caused by nearby obstructions.
- Far Shading Losses: From distant objects like mountains or neighboring buildings.
Step 4: Simulating Performance
With the 3D shading scene in place, users proceed to simulate the energy production of the PV system in PVsyst. This simulation incorporates parameters like:
- Panel orientation and tilt angles.
- Irradiation and weather data.
- Inverter performance.
Benefits of Integrating SketchUp and PVsyst
a) Improved Project Efficiency
The integration reduces the time spent on recreating models, enabling designers to focus on optimizing system performance.
b) Enhanced Accuracy
Detailed shading analysis leads to more accurate predictions of system performance, ensuring realistic energy production estimates.
c) Better Stakeholder Communication
SketchUp’s 3D visuals provide an excellent way to communicate design concepts to clients, investors, or regulatory bodies.
d) Streamlined Collaboration
Using SketchUp models within PVsyst fosters collaboration among architects, engineers, and solar designers, ensuring alignment across disciplines.
Challenges and Tips for Seamless Integration
Challenges
- File Compatibility: Exporting and importing files between SketchUp and PVsyst can occasionally lead to formatting issues.
- Complex Models: Highly detailed SketchUp models can increase the computational load in PVsyst.
- Learning Curve: Users need to be proficient in both tools for smooth integration.
Tips for Effective Integration
- Simplify SketchUp models by removing unnecessary details before exporting to PVsyst.
- Use dedicated plugins like Skelion for SketchUp, designed specifically for solar projects.
- Regularly update software versions to ensure compatibility.
Future Outlook: Evolving Integration Tools
As the renewable energy sector grows, software developers are investing in tools to bridge the gap between design and simulation platforms. Plugins and extensions that further integrate SketchUp and PVsyst are likely to improve in functionality and user-friendliness, driving innovation in solar design workflows.
The relationship between SketchUp and PVsyst is a testament to the power of combining versatile design tools with specialized simulation software. By leveraging the strengths of both platforms, solar designers can create accurate, efficient, and visually compelling PV system models. As tools for renewable energy continue to evolve, mastering the integration of SketchUp and PVsyst will remain a key skill for professionals in the solar energy industry.



