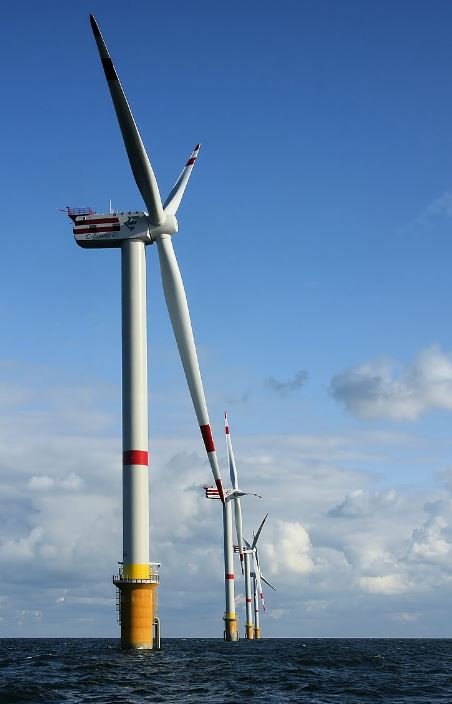
Wind energy is one of the types of renewable energy and there has been a great increase in the number of wind farms in recent years. Wind is the second largest energy source after solar energy.
So what is wind energy? How is electricity produced? Let’s examine it together.
What is Wind Energy
Wind is air movement caused by the sun’s unequal heating and cooling of the earth and the forces resulting from pressure differences. The kinetic energy of this air flow is called wind energy. The kinetic energy of the air mass turns into mechanical energy.
The method of using wind to generate electricity is known as wind energy. The kinetic energy in the wind is converted into mechanical power by wind turbines.
Wind energy is a renewable energy source that determines the wind’s entire power. Wind turbines convert kinetic energy to mechanical power, which is then transformed into electricity, which is then used as a source of energy.
Wind Turbine

Wind turbine is a system that converts the kinetic energy in the wind into electrical energy. Wind turbines are becoming an increasingly important source of intermittent renewable energy and are used in many countries to lower energy costs and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.
How do Wind Turbines Work?
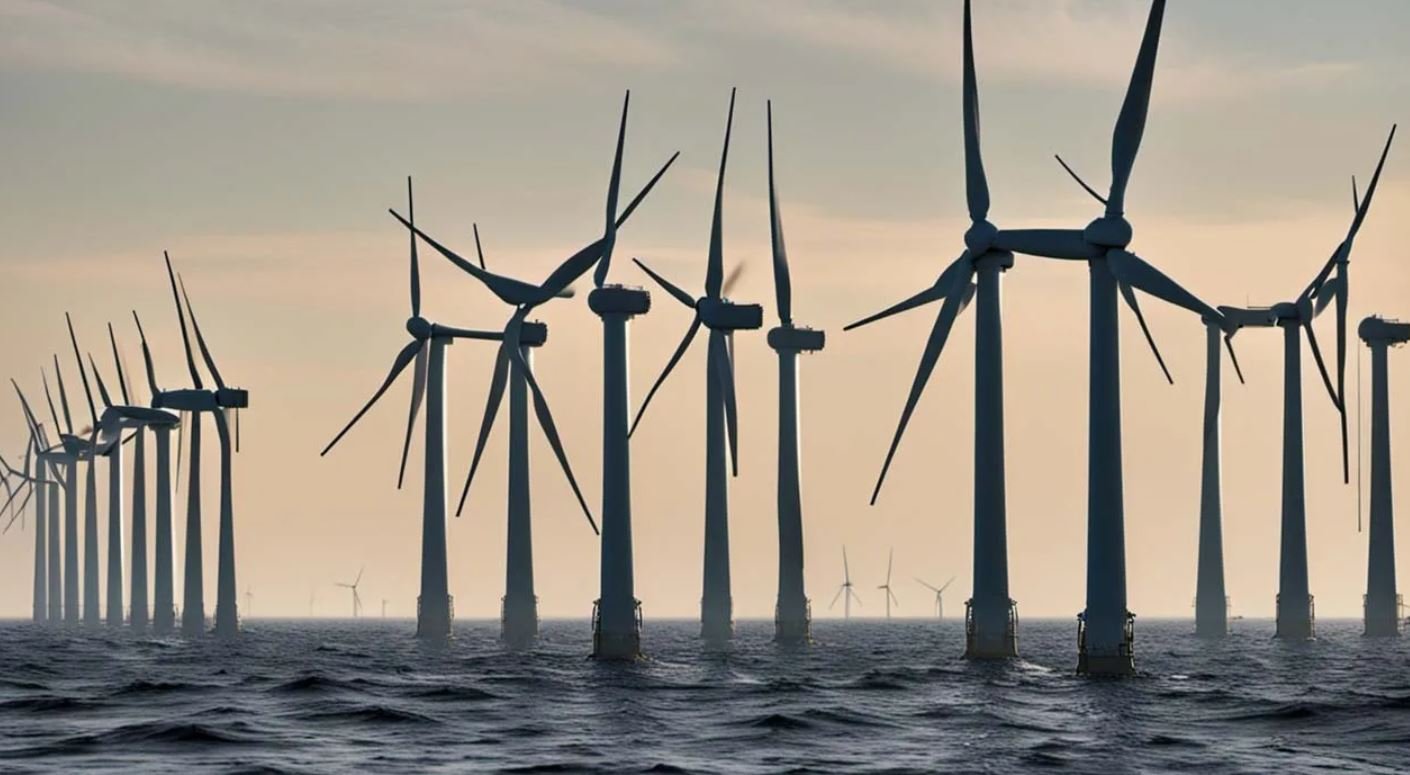

Wind turbines generate electricity by converting the kinetic energy of the wind into mechanical energy. A wind turbine’s basic components are the tower, rotor blades, and a nacelle that houses the gearbox and generator.
The wind is a type of solar energy caused by three simultaneous events:
- The sun heats the atmosphere unevenly.
- Surface irregularities of the Earth
- The earth’s rotation.
Wind energy and wind power, both the words describe the process of using wind to generate mechanical power or electricity. This mechanical power can be used for tasks such as grinding grain or pumping water, etc., or it can be converted into electricity by a generator.
A wind turbine converts wind energy into electricity by utilizing the aerodynamic force of the rotor blades, which function similarly to an airplane wing or helicopter rotor blade. When the wind blows across the blade, the air pressure on one side drops. Lift and drag are created by the difference in air pressure between the two sides of the blade.
The lift force is greater than the drag force, causing the rotor to spin. The rotor is connected to the generator either directly (if it is a direct drive turbine) or via a shaft and a series of gears (a gearbox), which speeds up the rotation and allows for a physically smaller generator. This conversion of aerodynamic force to generator rotation generates electricity.
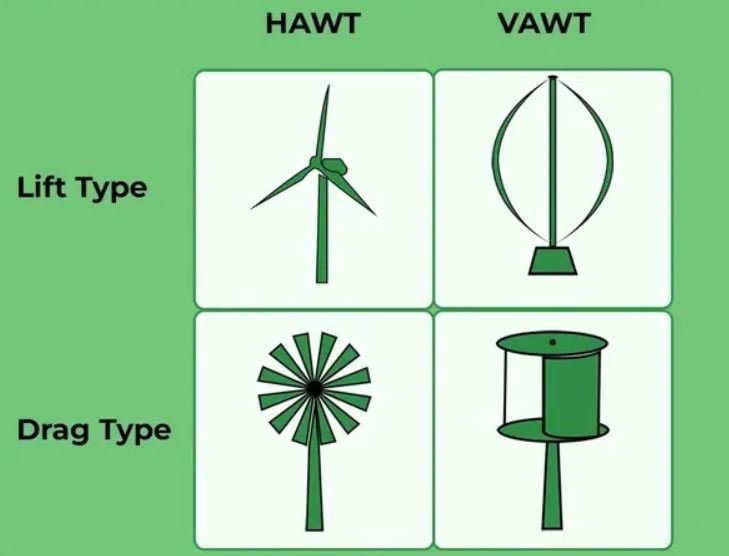
Types of Wind Turbines
There are many types of wind turbines, depending on the area to be used, the terrain, and the type of application. The most common is that it is divided into three different types.
- Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine (HAWT)
- Vertical Axis Wind Turbine (VAWT)
- Hybrid Wind Turbine
Wind Energy Formula
P = 1/2ρAv3
Where,
ρ = Density (kg/m3)
A = Swept Area (m2)
v = Wind Speed (m/s)
P = Power (W)
Derivation of Wind Energy Formula
The kinetic energy of an item with mass m and velocity v under constant acceleration is equal to the work done W in displacing that object from its original position.
Under a force F, rest to a distance s, i.e.
E = W = Fs
According to Newton’s Law, we have:
F = ma
Hence,
E = mas … (1)
Using the third equation of motion:
v2 = u2 + 2as
we get:
a = (v2 – u2)/2s
Since the initial velocity of the object is zero, i.e.
u = 0 , we get:
a = v2/2s
Substituting it in equation (1), we get that the
kinetic energy of a mass in motions is:
E = 1/2mv2……….(2)
The power in the wind is given by the rate of
change of energy:
P = dE/dt = 1/2v2dm/dt ……..(3)
As mass flow rate is given by:
dm/dt = ρAdx/dt
and the rate of change of distance is given by:
dx/dt = v
we get:
dm/dt = ρAv
Hence, from equation (3), the power can be
defined as:
P = 1/2ρAv3




